Rice can protect against obesity – if you’re eating the right kind
11/01/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
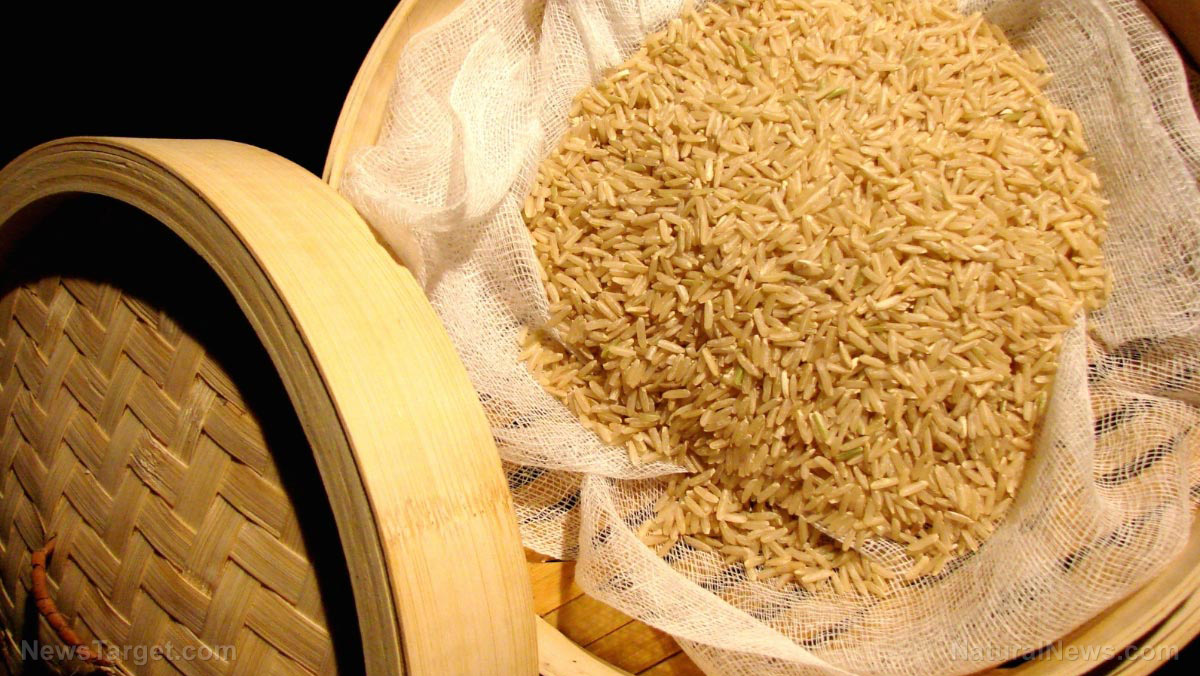

Rice is a staple food in many Asian countries and is usually consumed as part of every major meal. Not only is rice an excellent source of vitamins and minerals, but it is also loaded with fiber that supports digestive health. In a study presented early this year at the European Congress on Obesity in Glasgow, researchers examined the impact of rice consumption on health and found that obesity levels are significantly lower in countries that consume large quantities of rice, while in countries with lower average rice intake, obesity levels are soaring. The study’s findings further suggested that eating just the right amount of rice each day can protect against obesity, thanks to rice’s abundance in dietary fiber.
How rice can reduce the prevalence of obesity worldwide
Obesity, especially in many Western countries, is a growing epidemic. In the U.S. alone, nearly 40 percent of the population is battling this chronic disease. However, on the other side of the world, there are countries like Japan that have very low obesity rates (about 4.3 percent). So what is at the root of this discrepancy?
According to the study, which looked at the rice consumption rates of 136 countries, a higher prevalence of obesity can be found in populations that consume very little rice. On the other hand, even a moderate increase (about 50 g) in daily rice consumption could help prevent obesity and reduce its global prevalence by one percent.
Upon comparison of rice and calorie intake, obesity rates, and socioeconomic factors between several countries, the researchers found that those with higher rice consumption like Bangladesh, Laos, and Cambodia have lower rates of obesity, smoking, and health expenditure. Even after data were adjusted for certain risk factors, the association between obesity and rice intake remained the same. (Related: Brown rice and other whole grains can prevent type 2 diabetes.)
Sponsored: NEW Biostructured Silver First Aid Gel created by the Health Ranger combines three types of silver (ionic silver, colloidal silver, biostructured silver) with seven potent botanicals (rosemary, oregano, cinnamon and more) to create a breakthrough first aid silver gel. Over 50 ppm silver, verified via ICP-MS lab analysis. Made from 100% Texas rain water and 70% solar power. Zero chemical preservatives, fragrances or emulsifiers. See full details here.
Tomoko Imai, a professor from Doshisha Women’s College of Liberal Arts who led the research, concluded based on their data that a Japanese food or an Asian-food-style diet based on rice may help prevent obesity. He and his fellow researchers attributed this preventive effect on the fiber content of rice, which promotes digestive health, increases feelings of fullness, and prevents overeating.
Dietary fiber from plants and whole grains are also indigestible. Thus, they have the ability to make the body burn more calories in order to digest them. This, in turn, helps people shed weight. Many studies have reported that people who regularly eat fiber-rich foods enjoy lower body weights, cholesterol levels, and risks of developing chronic diseases.
“Rice is also low in fat and has a relatively low postprandial blood glucose level which suppresses insulin secretion,” Imai further explained. “However, there are also reports that people who overeat rice are more likely to develop metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Therefore, an appropriate amount of rice intake may prevent obesity.”
Which type of rice should you add to your diet?
There are many types of rice on the market. Each one has its own distinct characteristic and varies in terms of nutritional content. For instance, white rice, the most common type of rice, has pleasantly white-colored grains. Basmati rice, on the other hand, is aromatic and has long, slender grains. Glutinous rice, which is grown mainly in Southeast and East Asia, has opaque grains and is sticky once cooked. And brown rice, which is considered a whole grain, has a distinctive dirty brown color.
Among the many types of rice, brown rice is considered the healthiest and most nutritious. Unlike white rice, which is milled and polished to improve its physical properties and extend its shelf life, only the inedible hull is removed from brown rice, so the grain kernel remains intact. This means that brown rice still has its nutrient-rich core (germ) and fiber-filled outer layer (bran), which are no longer present in refined white rice.
Brown rice contains plenty of nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fiber, protein, calcium, iron, manganese, and vitamins A, B-complex, and C. Brown rice is also gluten-free and only has trace amounts of fat and sodium, making it perfect even for people with various health conditions, such as diabetes and celiac disease.
To reduce your risk of obesity, add brown rice to your daily diet. You can use rice together with vegetables as your source of fiber and essential nutrients. You can also opt for other whole grain rice varieties like black rice, gold rice, and red rice. These only differ from brown rice in terms of the color of their outer layers.
Learn what other benefits you can get from whole grains by visiting Food.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anti-obesity, Basmati rice, black rice, brown rice, clean food, diabetes, dietary fiber, digestion, digestive health, fightobesity, food cures, food is medicine, food science, functional food, gluten free, glutinous rice, gold rice, minerals, natural cures, natural medicine, nutrients, obesity, prevention, red rice, research, rice, rice bran, rice germ, satiety, vitamins, weight loss, white rice, whole grains
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
Natural.News is a fact-based public education website published by Natural News Features, LLC.
All content copyright © 2018 by Natural News Features, LLC.
Contact Us with Tips or Corrections
All trademarks, registered trademarks and servicemarks mentioned on this site are the property of their respective owners.