Top 10 functional foods for relieving inflammation
07/21/2015 / By Carol Young

Refined and processed foods can trigger an immune response that leads to inflammation. Chronic inflammation can contribute to many diseases and disorders from atherosclerosis to Alzheimer’s disease. Some foods can reduce inflammation and protect against chronic inflammation. These foods are also full of important minerals, fiber and vitamins that the body needs for optimal health.
Ginger and turmeric
Turmeric and ginger have anti-inflammatory properties and have been used in traditional medicine for many, many years. Ginger has the anti-inflammatory compound gingerol, which provides free radical protection.
Onions and garlic
Garlic shuts off pathways that lead to inflammation according to some studies, and onions also have the phytonutrient quercetin, which breaks down free radicals. Eating onions and turmeric together also improves the absorption of curcumin, a powerful antioxidant.
Fatty fish
Fatty fish are usually cold-water fish and are also known as oily fish. Oily fish is high in omega-3 fatty acids which have been shown to reduce inflammation. Examples of oily fish include salmon, tuna, sardines and mackerel. Avoid farm-raised fish and always choose fish which have been sustainably caught. Mercury is a concern with seafood, but salmon and canned light tuna have lower mercury levels.
There is both nutritional and ethical rationale for why wild-caught fish is better than farm-raised fish. In a 2004 study published in the journal Science, researchers found that farmed fish had higher amounts of contaminants than wild fish. According to the National Humane Education Society, farmed fish often live in small enclosures that are breeding grounds for parasites and disease. The fish are often starved before they are brought to the slaughterhouse and are killed by being bashed on the head, having their gills slit or being suffocated.
Mother Nature's micronutrient secret: Organic Broccoli Sprout Capsules now available, delivering 280mg of high-density nutrition, including the extraordinary "sulforaphane" and "glucosinolate" nutrients found only in cruciferous healing foods. Every lot laboratory tested. See availability here.
Whole grains instead of refined grains
Whole grains have more fiber and there is a link between reduced inflammation and whole grain consumption. Whole grains you may want to try include brown rice, steel cut oats, buckwheat and bulgur wheat. Refined grains (white bread, white rice and de-germed cornmeal) on the other hand increase inflammation; refined grain intake is positively linked to elevated levels of an inhibitor which is directly associated with atherosclerosis.
Delicious dark leafy greens
Broccoli, spinach, kale, collard greens and rainbow chard are full of vitamin E, which could protect the body from pro-inflammatory cytokines. Dark green and cruciferous vegetables have very high concentrations of minerals and phytochemicals. Green leafy vegetables are also high in magnesium, which is good for blood pressure, and they are a low-glycemic food, which means they will not cause an insulin spike. Try blending leafy greens in a smoothie with ginger and berries. Or, cook a leafy green such as spinach with chickpeas, smoked paprika and olive oil for a Mediterranean-style dish.
Nuts
Almonds are full of fiber, vitamin E and calcium; walnuts are full of omega-3s. All nuts have antioxidants which fight inflammation. Nuts are a staple of the Mediterranean diet, which is also known to be a great way of eating to reduce inflammation. While nuts are high in fat, it is a heart-healthy fat, and eating a handful of unsalted nuts a day is a good way to lower your risk of heart disease.
Peppers
Bell peppers have capsaicin in them, which is a chemical that can reduce pain and inflammation. It is best to eat a mix of bell peppers in different shades. Bell peppers are in the top 100 list of the world’s healthiest foods, according to WHFoods.org, and are also full of important antioxidants that can help fight disease.
Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a nightshade vegetable and may reduce inflammation in certain individuals. They are high in lycopene, which can reduce inflammation in the lungs and throughout the rest of the body. Applying heat to tomatoes increases the lycopene content and total antioxidant content, according to a study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry by Veronica Dewanto and fellow researchers from Cornell University.
Beets
Beetroot juice can reduce inflammation and is a popular drink for athletes. In fact, Olympic athletes were guzzling beetroot juice at the Summer London Olympics in 2012 for a performance boost. Beets are high in antioxidants, fiber, vitamin C and betalains. A 2001 study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry concluded that consuming red beet products regularly could provide against “certain oxidative stress-related disorders in humans.”
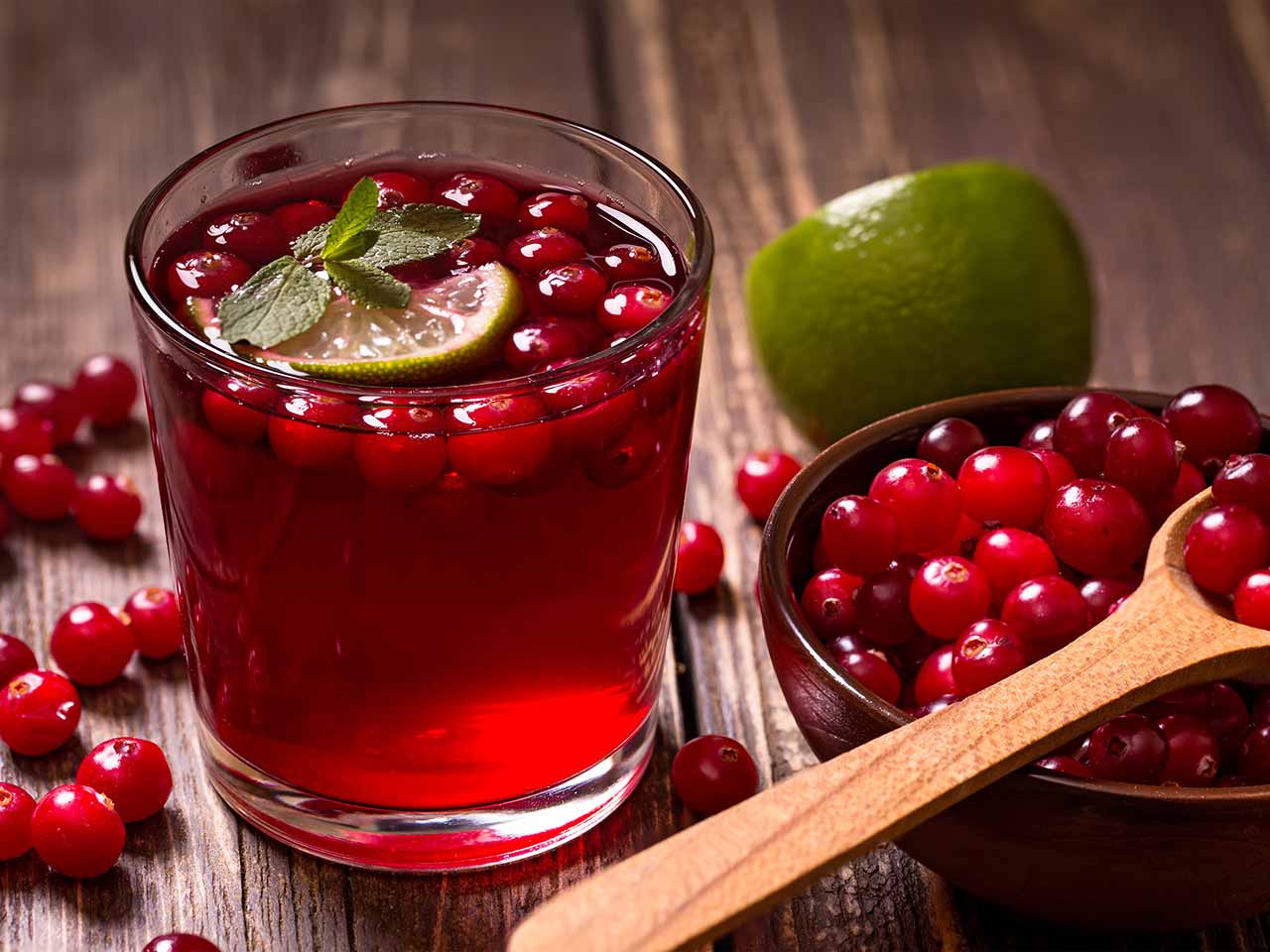
Berries
Berries are high in anthocyanins, which are powerful antioxidants that are known to be anti-inflammatory. The bright color of berries are a testament to these antioxidants, and blueberries in particular can protect against intestinal inflammation. Strawberries, blueberries and cranberries are good choices for reducing inflammation in the body.
Sources:
http://www.augerchiro.com[PDF]
http://ucanr.edu[PDF]
Tagged Under: antioxidants, free radiclas, functional foods, inflammation